Suppose that a population develops according to the logistic equation: a captivating exploration into the intricacies of population growth. This equation, a cornerstone of population ecology, unveils the intricate dance between population size, environmental constraints, and the inexorable forces that shape its trajectory.
Join us as we delve into the depths of this mathematical marvel, unraveling its significance and unlocking the secrets of population dynamics.
The logistic equation, a brainchild of the renowned mathematician Pierre François Verhulst, serves as a cornerstone for modeling population growth. It encapsulates the interplay between intrinsic growth rate, carrying capacity, and the ever-present environmental factors that modulate population dynamics. Through this equation, we gain insights into the stages of population growth, from the initial surge to the eventual attainment of equilibrium.
1. The Logistic Equation
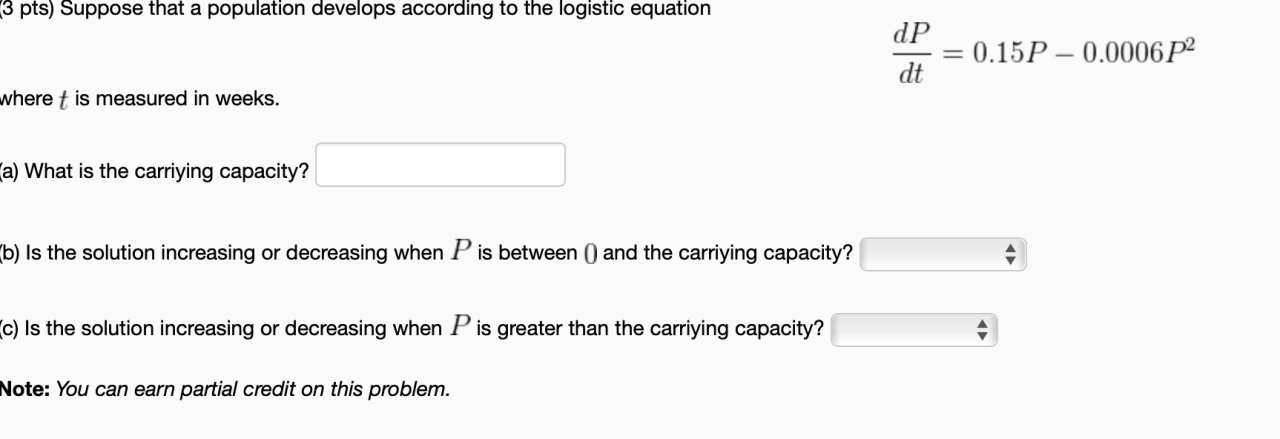
The logistic equation is a mathematical model that describes the growth of a population over time. It is given by the following differential equation:
$\fracdNdt = rN(1-\fracNK)$
where:
- Nis the population size at time t
- ris the intrinsic growth rate
- Kis the carrying capacity
The logistic equation captures the idea that population growth is initially exponential but eventually slows down as the population approaches its carrying capacity. The carrying capacity represents the maximum population size that can be sustained by the environment.
2. Population Growth Dynamics

The logistic equation describes the following stages of population growth:
- Lag phase:Population growth is slow as the population establishes itself in the environment.
- Exponential phase:Population growth is rapid as the population size increases exponentially.
- Logarithmic phase:Population growth slows down as the population approaches its carrying capacity.
- Stationary phase:Population growth reaches zero as the population size stabilizes at the carrying capacity.
3. Environmental Factors
Environmental factors can influence population growth according to the logistic equation.
- Resource availability:Limited resources, such as food and water, can reduce the carrying capacity and slow down population growth.
- Competition:Competition for resources between individuals can reduce the intrinsic growth rate and limit population growth.
4. Applications and Limitations
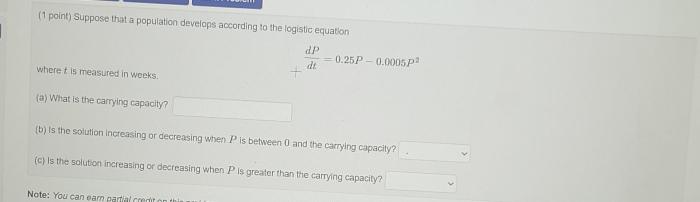
The logistic equation has applications in population ecology and epidemiology.
- Population ecology:The equation can be used to predict the size and growth of animal and plant populations.
- Epidemiology:The equation can be used to model the spread of infectious diseases and predict the number of infected individuals over time.
However, the logistic equation has limitations:
- It assumes a constant carrying capacity, which may not always be true.
- It does not account for factors such as immigration and emigration.
5. Extensions and Modifications

The logistic equation can be modified to account for additional factors:
- Immigration and emigration:These factors can be incorporated into the equation to account for the movement of individuals into and out of the population.
Alternative population growth models include:
- Gompertz equation:This model accounts for a declining intrinsic growth rate over time.
- Richards equation:This model accounts for a variable carrying capacity that changes over time.
Quick FAQs: Suppose That A Population Develops According To The Logistic Equation
What is the logistic equation?
The logistic equation is a mathematical model that describes the growth of a population over time, taking into account both the intrinsic growth rate and the carrying capacity of the environment.
What are the key parameters in the logistic equation?
The key parameters in the logistic equation are the intrinsic growth rate (r) and the carrying capacity (K). The intrinsic growth rate represents the rate at which the population would grow in the absence of any environmental constraints, while the carrying capacity represents the maximum population size that can be supported by the environment.
What are the stages of population growth represented by the logistic equation?
The logistic equation represents three stages of population growth: exponential growth, logistic growth, and equilibrium. Exponential growth occurs when the population size is small and the environment is not limiting. Logistic growth occurs when the population size is increasing, but the rate of growth is slowing down as the population approaches the carrying capacity.
Equilibrium occurs when the population size has reached the carrying capacity and the rate of growth is zero.