Type of cell division crossword clue – The enigmatic “Type of cell division” crossword clue beckons us on a captivating journey into the realm of cellular biology, where we will decipher its hidden meanings and uncover the fundamental processes that govern cell reproduction.
Cell division, a ubiquitous phenomenon in living organisms, encompasses a diverse array of mechanisms that orchestrate the creation of new cells, facilitate growth, and ensure the continuity of life. Mitosis and meiosis, two prominent types of cell division, play distinct roles in the life cycle of eukaryotic cells, and their intricate differences hold the key to understanding the intricate workings of cellular reproduction.
Crossword Clue Analysis
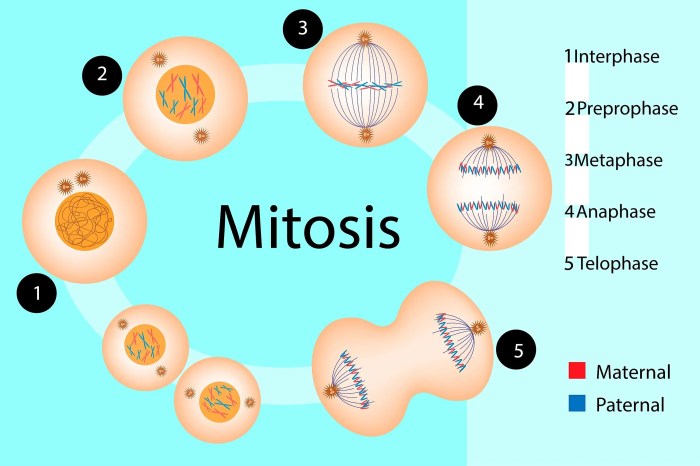
The crossword clue “Type of cell division” can refer to various types of cell division processes that occur in different organisms and contexts.
Possible interpretations of the clue include:
- Binary Fission:A type of cell division in prokaryotic organisms where one cell divides into two identical daughter cells.
- Mitosis:A type of cell division in eukaryotic organisms where one cell divides into two identical daughter cells, maintaining the same number of chromosomes.
- Meiosis:A type of cell division in eukaryotic organisms that produces gametes (sex cells) with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
Potential answers that fit the clue could include:
- BINARY FISSION
- MITOSIS
- MEIOSIS
Mitosis vs. Meiosis
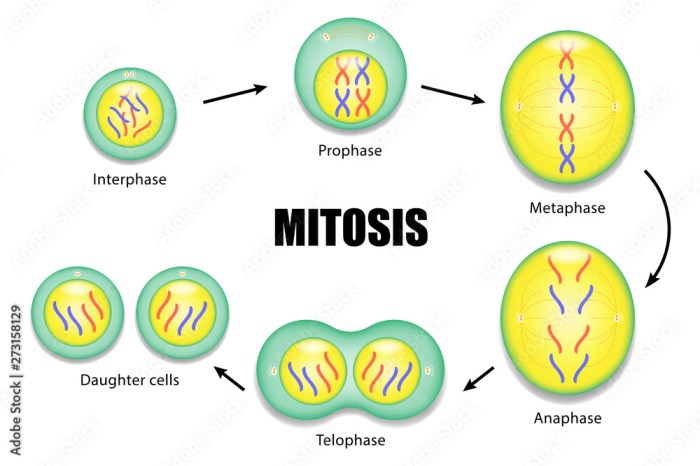
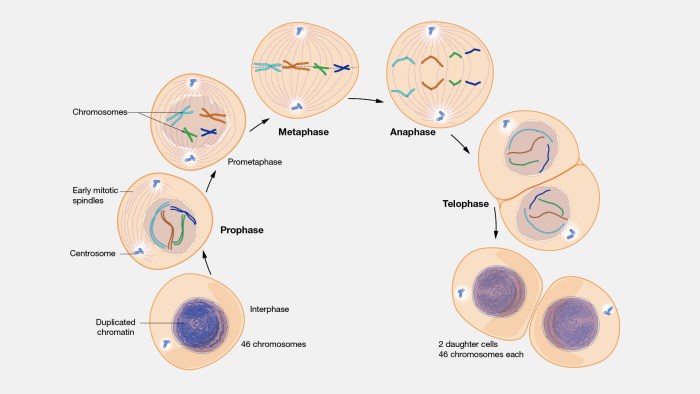
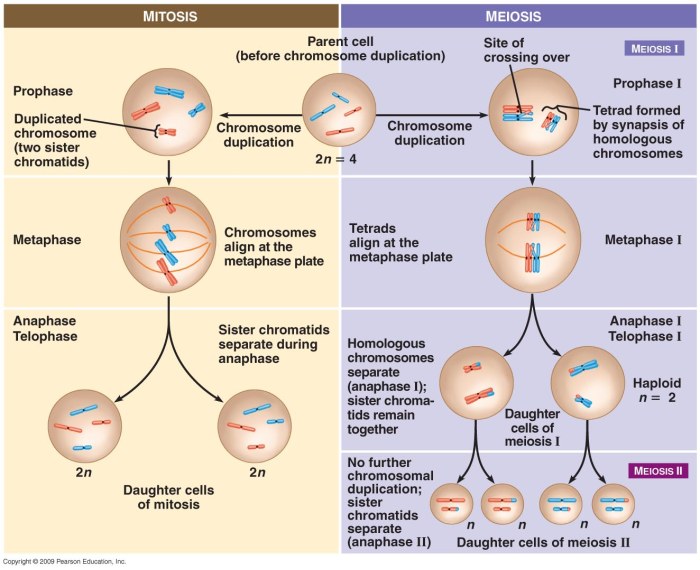
Mitosis and meiosis are two distinct types of cell division that occur in eukaryotic organisms. Mitosis is a process of cell division that produces two identical daughter cells, while meiosis is a process that produces four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
Mitosis is used for growth and repair of tissues, while meiosis is used for the production of gametes (sex cells). Mitosis occurs in somatic cells, which are all the cells in the body except for the gametes, while meiosis occurs in germ cells, which are the cells that give rise to gametes.
Purpose
The purpose of mitosis is to produce two identical daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell. This process is used for growth and repair of tissues. The purpose of meiosis is to produce four daughter cells that each have half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
This process is used for the production of gametes.
Process
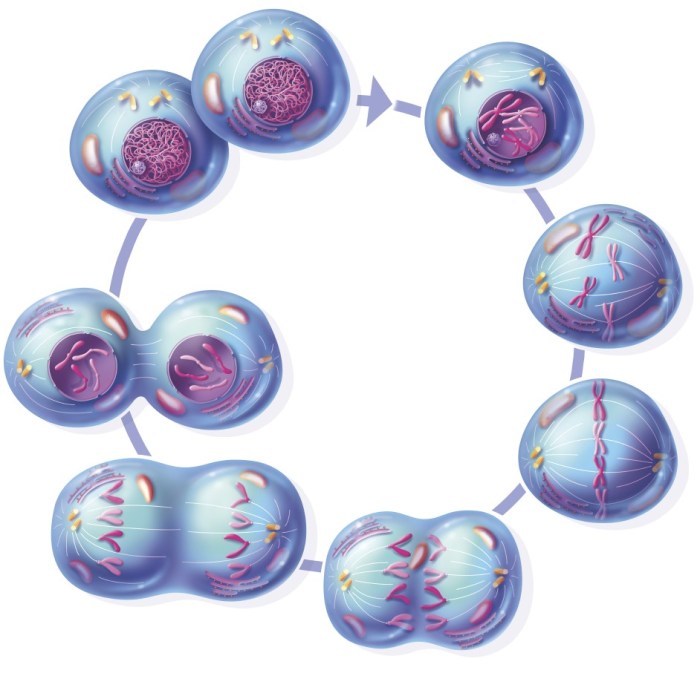
Mitosis occurs in four phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During prophase, the chromosomes become visible and the nuclear envelope breaks down. During metaphase, the chromosomes line up in the center of the cell. During anaphase, the chromosomes are separated and pulled to opposite ends of the cell.
During telophase, two new nuclear envelopes form around the chromosomes and the cell membrane pinches in the middle, dividing the cell into two daughter cells.
Meiosis occurs in two phases: meiosis I and meiosis II. During meiosis I, the chromosomes become visible and the nuclear envelope breaks down. The chromosomes then pair up and exchange genetic material through a process called crossing-over. The chromosomes then line up in the center of the cell and are separated, with one chromosome from each pair going to each daughter cell.
During meiosis II, the chromosomes line up in the center of the cell and are separated again, with one chromosome from each pair going to each daughter cell. This results in four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
Outcomes
The outcomes of mitosis are two identical daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell. The outcomes of meiosis are four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. These daughter cells are then able to fuse with other gametes to form zygotes, which develop into new organisms.
The following table summarizes the key differences between mitosis and meiosis:
| Characteristic | Mitosis | Meiosis |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Growth and repair of tissues | Production of gametes |
| Process | Four phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase | Two phases: meiosis I and meiosis II |
| Outcomes | Two identical daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell | Four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell |
Cell Cycle and Cell Division: Type Of Cell Division Crossword Clue
The cell cycle is a continuous process of growth, replication, and division that occurs in all living cells. It consists of two main phases: interphase and mitosis. During interphase, the cell grows and replicates its DNA. Mitosis is the process by which the cell divides into two identical daughter cells.Cell
division is an essential process for growth, development, and repair. It allows organisms to increase in size, replace damaged cells, and reproduce.
Relationship between Cell Cycle and Cell Division
Cell division is a critical part of the cell cycle. It occurs during the M phase (mitosis and cytokinesis) of the cell cycle. During the M phase, the cell divides into two identical daughter cells. The daughter cells then enter the G1 phase of the cell cycle and begin the process of growth and DNA replication again.
Cell Cycle Flowchart, Type of cell division crossword clue
The following flowchart illustrates the cell cycle and its stages:[Flowchart:Start: G1 Phase
- > S Phase
- > G2 Phase
- > M Phase
- > Cytokinesis
- > G1 Phase (new cell cycle)]
Examples and Applications
Cell division plays a vital role in numerous biological processes and has a wide range of applications in various fields. It is essential for growth, development, repair, and reproduction in all living organisms.
Here are some specific examples of how cell division is used in real-world applications:
Medical Applications
- Tissue Engineering:Cell division is used to grow new tissues and organs for transplantation, such as skin grafts and heart valves.
- Cancer Treatment:Cell division is targeted by chemotherapy and radiation therapy to kill cancer cells.
- Stem Cell Therapy:Stem cells, which have the ability to divide and differentiate into various cell types, are used to treat a range of diseases and conditions.
Agriculture and Biotechnology
- Plant Breeding:Cell division is utilized in plant tissue culture to propagate new plants with desired traits, such as resistance to pests or improved yield.
- Genetic Engineering:Cell division is used to insert or modify genes in organisms, creating genetically modified crops and animals with enhanced characteristics.
Research and Development
- Cell Biology:Cell division is studied to understand the fundamental mechanisms of life and develop treatments for diseases.
- Drug Discovery:Cell division is used to screen potential drugs for their effects on cell growth and proliferation.
- Biotechnology:Cell division is utilized to produce proteins and other biomolecules for use in pharmaceuticals, diagnostics, and industrial applications.
Question Bank
What is the primary difference between mitosis and meiosis?
Mitosis produces two genetically identical daughter cells, while meiosis produces four genetically diverse daughter cells.
How does cell division contribute to tissue repair?
Cell division enables the replacement of damaged or lost cells, facilitating tissue regeneration and repair.
What role does cell division play in embryonic development?
Cell division is essential for the growth and differentiation of an embryo, giving rise to the various tissues and organs that form a complex organism.