Katrina drinks 0.5 gallons of water – Katrina’s decision to consume 0.5 gallons of water daily has sparked intrigue and raised questions about the significance of water intake. This article delves into the topic, examining the potential health benefits, the role of water in maintaining hydration, and the importance of consuming clean and safe water.
By exploring Katrina’s water consumption habits, we gain insights into the crucial role water plays in our overall well-being.
Water is essential for life, and consuming an adequate amount is crucial for maintaining optimal health. This article explores the benefits of consuming 0.5 gallons of water per day, including improved hydration, enhanced cognitive function, and reduced risk of chronic diseases.
Water Consumption

Water is an essential nutrient that plays a vital role in various bodily functions, including hydration, waste elimination, and temperature regulation. Consuming an adequate amount of water is crucial for maintaining optimal health and well-being.
Significance of Daily Water Intake
Daily water intake is essential for:
- Maintaining fluid balance in the body
- Transporting nutrients and oxygen to cells
- Regulating body temperature
- Lubricating joints
- Protecting organs and tissues
Potential Health Benefits of Consuming 0.5 Gallons of Water per Day
Consuming 0.5 gallons of water per day may offer numerous health benefits, including:
- Improved hydration
- Reduced risk of dehydration
- Enhanced athletic performance
- Improved skin health
- Boosted energy levels
Incorporating 0.5 Gallons of Water into a Daily Routine
To incorporate 0.5 gallons of water into a daily routine, consider the following strategies:
- Drink a glass of water upon waking
- Carry a water bottle throughout the day and sip regularly
- Consume water-rich fruits and vegetables, such as watermelon and cucumbers
- Avoid sugary drinks and opt for water instead
Hydration and Health
Water plays a crucial role in maintaining hydration, a vital aspect of overall health. It constitutes approximately 60% of the human body and participates in numerous physiological processes.
Maintaining adequate hydration is essential for optimal bodily functions. Water facilitates the transportation of nutrients, hormones, and oxygen throughout the body, aiding in metabolic processes and waste removal. It also regulates body temperature, lubricates joints, and protects tissues and organs.
Consequences of Dehydration
Dehydration occurs when the body loses more water than it takes in, leading to a water deficit. This can result from inadequate fluid intake, excessive sweating, or certain medical conditions. Dehydration can have detrimental effects on physical and cognitive performance.
- Mild dehydration(1-2% loss of body weight): Fatigue, dizziness, headache, dry mouth, and thirst.
- Moderate dehydration(3-6% loss of body weight): Increased heart rate, decreased blood pressure, muscle cramps, and impaired coordination.
- Severe dehydration(7% or more loss of body weight): Confusion, seizures, organ failure, and even death.
Water Intake and Overall Health
Numerous studies have established a strong correlation between water intake and overall health. Adequate hydration supports:
- Improved cognitive function:Water enhances alertness, concentration, and memory.
- Reduced risk of chronic diseases:Studies suggest that sufficient water intake may lower the risk of certain chronic conditions, such as heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes.
li> Weight management:Drinking water before meals can promote satiety and reduce calorie intake.
Water Sources and Quality

Access to clean and safe drinking water is crucial for maintaining good health and preventing waterborne diseases. Water sources vary, and their quality can differ significantly, impacting the health of individuals who consume them.
Water Sources
- Surface water:Rivers, lakes, and streams are common sources of surface water. They are easily accessible but can be contaminated with pollutants from agricultural runoff, industrial discharge, or sewage.
- Groundwater:Water stored underground in aquifers is generally cleaner than surface water, as it is naturally filtered through soil and rock layers. However, groundwater can still become contaminated by pollutants that seep into the ground, such as pesticides or fertilizers.
- Rainwater:Rainwater can be collected and stored for drinking, but it is important to ensure that the collection system is clean and free of contaminants. Rainwater can be acidic due to dissolved carbon dioxide and may require treatment before consumption.
- Desalinated water:In areas with limited access to freshwater,海水 desalination plants can convert seawater into drinkable water. Desalination is an energy-intensive process that can be expensive.
Importance of Clean and Safe Water
Consuming clean and safe water is essential for maintaining good health and preventing waterborne diseases. Contaminated water can contain harmful bacteria, viruses, parasites, and chemicals that can cause a range of illnesses, including diarrhea, vomiting, and more severe conditions such as typhoid fever or cholera.
Potential Contaminants in Water and Their Health Implications
- Microorganisms:Bacteria (e.g., E. coli, Salmonella), viruses (e.g., norovirus, hepatitis A), and parasites (e.g., Giardia, Cryptosporidium) can contaminate water sources and cause gastrointestinal illnesses.
- Chemicals:Industrial pollutants (e.g., heavy metals, pesticides), agricultural runoff (e.g., nitrates), and disinfection byproducts (e.g., trihalomethanes) can leach into water sources and pose health risks, including cancer, developmental problems, and reproductive issues.
- Natural contaminants:Arsenic, fluoride, and other naturally occurring substances can be present in groundwater in certain regions and can cause health problems if consumed in excessive amounts.
Water Filtration and Purification

Water filtration and purification are essential processes for ensuring the safety and quality of drinking water. Various methods are available, each with its unique effectiveness and cost implications.
The following table provides a comparison of common water filtration and purification methods:
| Method | Effectiveness | Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Activated Carbon Filter | Removes chlorine, organic compounds, and some heavy metals | Low |
| Reverse Osmosis | Removes most contaminants, including bacteria, viruses, and dissolved solids | High |
| Ultraviolet (UV) Disinfection | Kills bacteria and viruses | Medium |
| Chlorination | Kills bacteria and viruses | Low |
| Distillation | Removes all contaminants | High |
Benefits of Using Filtered or Purified Water
Consuming filtered or purified water offers several benefits:
- Improved taste and odor
- Reduced risk of waterborne diseases
- Protection against harmful contaminants
- Enhanced hydration and overall health
By choosing a suitable filtration or purification method, individuals can access safe and clean drinking water, promoting their health and well-being.
Water Conservation: Katrina Drinks 0.5 Gallons Of Water
Water conservation is a critical aspect of sustainable water management. It involves the adoption of practices and strategies to reduce water consumption and preserve water resources for future generations.
Water scarcity is a growing concern worldwide, driven by factors such as population growth, urbanization, and climate change. Sustainable water management practices are essential to mitigate the environmental impact of water scarcity and ensure the long-term availability of clean water.
Tips for Reducing Water Consumption
- Install low-flow showerheads and faucets to reduce water usage during showers and handwashing.
- Fix leaky faucets and pipes promptly to prevent water wastage.
- Use water-efficient appliances, such as washing machines and dishwashers, which consume less water per cycle.
- Water plants during cooler hours of the day to minimize evaporation.
- Consider using drought-tolerant plants in landscaping to reduce water needs for irrigation.
- Collect rainwater for non-potable purposes, such as watering plants or washing cars.
- Take shorter showers and turn off the water while brushing teeth or shaving.
- Use a broom or blower instead of a hose to clean driveways or sidewalks.
- Check water bills regularly to monitor water usage and identify potential leaks or areas for improvement.
Environmental Impact of Water Scarcity, Katrina drinks 0.5 gallons of water
Water scarcity can have significant environmental consequences, including:
- Reduced water availability for ecosystems, leading to biodiversity loss and habitat degradation.
- Increased water pollution due to reduced dilution of contaminants.
- Land subsidence and soil erosion in areas where groundwater is over-extracted.
- Conflicts and disputes over water resources, both within and between countries.
FAQs
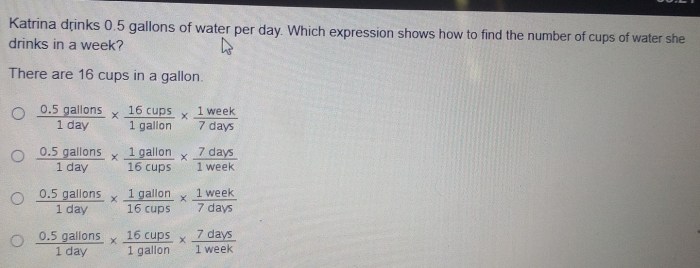
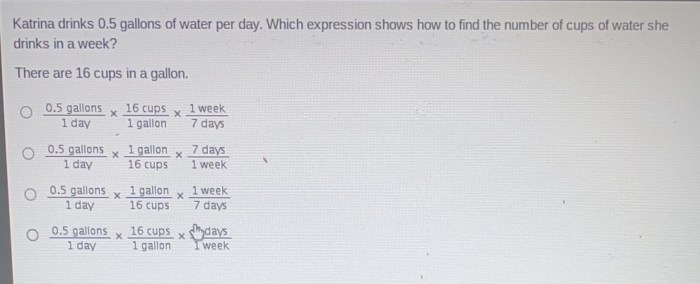
How can I incorporate 0.5 gallons of water into my daily routine?
To incorporate 0.5 gallons of water into your daily routine, you can set reminders, carry a reusable water bottle, and consume water-rich fruits and vegetables.
What are the signs of dehydration?
Signs of dehydration include fatigue, dizziness, headache, dry mouth, and decreased urine output.
Is it safe to drink tap water?
The safety of tap water depends on the local water treatment system. It is recommended to check with your local water supplier or test your tap water to ensure its quality.